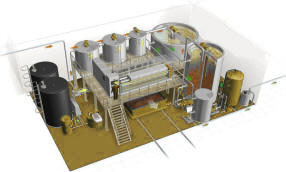
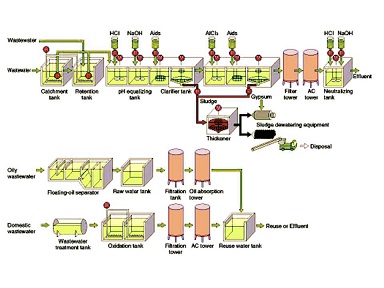
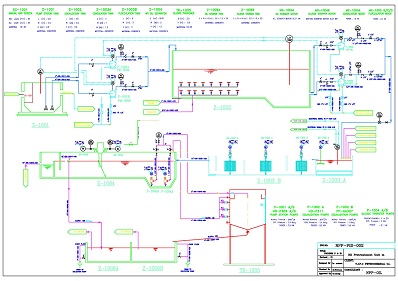
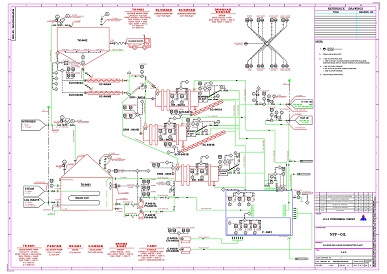
waste water treatment plant
The major aim of wastewater treatment is to remove as much of the suspended solids as possible before the remaining water, called effluent, is discharged back to the environment. As solid material decays, it uses up oxygen, which is needed by the plants and animals living in the water.
Usually wastewater treatment will involve collecting the wastewater in a central, segregated location (the Wastewater Treatment Plant) and subjecting the wastewater to various treatment processes. Most often, since large volumes of wastewater are involved, treatment processes are carried out on continuously flowing wastewaters (continuous flow or "open" systems) rather than as "batch" or a series of periodic treatment processes in which treatment is carried out on parcels or "batches" of wastewaters. While most wastewater treatment processes are continuous flow, certain operations, such as vacuum filtration, involving as it does, storage of sludge, the addition of chemicals, filtration and removal or disposal of the treated sludge, are routinely handled as periodic batch operations.
"Primary treatment" removes about 60 percent of suspended solids from wastewater. This treatment also involves aerating (stirring up) the wastewater, to put oxygen back in. Secondary treatment removes more than 90 percent of suspended solids.
A complete treatment system may consist of the application of a number of physical, chemical and biological processes to the wastewater.
Wastewater Treatment Methods
Physical : Sedimentation (Clarification),Screening,Aeration,Filtration,Flotation and Skimming,Degassification,Equalization
Chemical : Chlorination,Ozonation, Neutralization, Coagulation, Adsorption, Ion Exchange
Biological :Aerobic ,Activated Sludge Treatment Methods,Trickling Filtration, Oxidation Ponds, Lagoon
 |
 |
 |
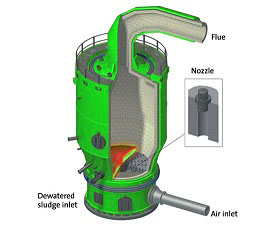
sludge and liquid incinerator plant
Incineration and other high temperature waste treatment systems are described as "thermal treatment".Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves the combustion of organic substances contained in waste materials. Incineration of waste materials converts the waste into ash, flue gas, and heat. The ash is mostly formed by the inorganic constituents of the waste, and may take the form of solid lumps or particulates carried by the flue gas. The flue gases must be cleaned of gaseous and particulate pollutants before they are dispersed into the atmosphere.
The European Union (EU) has introduced measures to prevent or reduce air, water and soil pollution caused by the incineration or co-incineration of waste, as well as the resulting risk to human health. These measures specifically require a permit be obtained for incineration and co-incineration plants, and emission limits for certain pollutants released to air or to water.
Because toxic gasses of the waste incinerator can have a serious impact on the human health it is a requirement to continuously monitor them at the exit of the stack.In case the monitoring shows too high values, the installation shuts down automatically.
The emission monitoring system measures in
real time an half hour average and a daily average of the emission levels in
the stack.
These are some reference norms:
| Units | EU (Daily) |
EU (Hrly) |
EU (4 Hr) |
EU Overall |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ash / Particulates | mg/Nm3 | 5 | 10 | 5 | |
| HF | " | - | |||
| HCl | " | 5 | 10 | 5 | |
| CO | " | 50 | 100 | 50 | |
| NOx | " | 100 | 200 | 100 | |
| SOx | " | 25 | 50 | 25 | |
| Cd | " | 0,05 | 0,05 | ||
| Hg | " | 0,05 | 0,05 | ||
| Pb | " | - | |||
| Heavy Metals | " | - | |||
| Dioxin / Furans | ng/Nm3 | 0,10 | 0,10 | ||
| Total Organics | mg/Nm3 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
 |
|
 |
Parameters for wastewater, drinking water, process water , raw water
QUALITY OF RAW WASTEWATER AND PRIMARY EFFLUENT AT SELECTED TREATMENT PLANTS IN CALIFORNIA
|
Quality parameters (mg/l, except as otherwise indicated) |
City of Davis |
San Diego |
Los Angeles County Joint Plant |
||||
|
Raw wastewater |
Primary effluent |
Raw wastewater |
Primary effluent |
Raw wastewater |
Primary effluent |
||
|
Biochemical oxygen demand,BOD5 |
112 |
73 |
184 |
134 |
- |
204 |
|
|
Total organic carbon |
63.8 |
40.6 |
64.8 |
52.3 |
- |
- |
|
|
Suspended solids |
185 |
72 |
200 |
109 |
- |
219 |
|
|
Total nitrogen |
43.4 |
34.7 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
|
NH3-N |
35.6 |
26.2 |
21.0 |
20.0 |
- |
39.5 |
|
|
NO-N |
0 |
0 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
Org-N |
7.8 |
8.5 |
- |
- |
- |
14.9 |
|
Total phosphorus |
- |
7.5 |
- |
10.2 |
- |
11.2 |
|
|
|
Ortho-P |
- |
7.5 |
11.2 |
|
- |
|
|
pH (unit) |
7.7 |
- |
7.3 |
7.3 |
- |
- |
|
|
Cations: |
|||||||
|
|
Ca |
- |
- |
- |
- |
78.8 |
- |
|
|
Mg |
- |
- |
- |
- |
25.6 |
- |
|
|
Na |
- |
- |
- |
- |
357 |
359 |
|
|
K |
- |
- |
- |
- |
19 |
19 |
|
Anions: |
|||||||
|
|
SO4 |
- |
|
160 |
|
270 |
|
|
|
Cl |
- |
|
120 |
|
397 |
|
|
Electrical conductivity, dS/m |
2.52 |
2.34 |
|
|
2.19 |
- |
|
|
Total dissolved solids |
- |
- |
829 |
821 |
1404 |
1406 |
|
|
Soluble sodium percentage, % |
- |
|
- |
|
70.3 |
|
|
|
Sodium adsorption ratio |
- |
- |
- |
- |
8.85 |
6.8 |
|
|
Boron (B) |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.68 |
1.5 |
|
|
Alkalinity (CaCO3) |
- |
- |
- |
|
322 |
332 |
|
|
Hardness (CaCO3) |
- |
|
- |
|
265 |
|
|
QUALITY OF SECONDARY EFFLUENT AT SELECTED WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANTS IN CALIFORNIA
|
Quality parameter (mg/I except as otherwise indicated) |
Plant location |
||||
|
Trickling filters |
Activated sludge |
||||
|
Chino Basin MWD (No. 1) |
Chino Basin MWD (No. 2) |
Santa Rosa Laguna |
Montecito Sanitary District |
||
|
Biochemical oxygen demand, BOD5 |
21 |
8 |
- |
11 |
|
|
Chemical oxygen demand |
- |
- |
27 |
- |
|
|
Suspended solids |
18 |
26 |
- |
13 |
|
|
Total nitrogen |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
|
NH3-N |
25 |
11 |
10 |
1.4 |
|
|
NO3-N |
0.7 |
19 |
8 |
5 |
|
|
Org-N |
- |
- |
1.7 |
- |
|
Total phosphorus |
- |
- |
12.5 |
- |
|
|
Ortho-P |
- |
- |
3.4 |
- |
|
|
pH (unit) |
- |
- |
- |
7.6 |
|
|
Cations: |
|||||
|
|
Ca |
43 |
55 |
41 |
82 |
|
|
Mg |
12 |
18 |
18 |
33 |
|
|
Na |
83 |
102 |
94 |
- |
|
|
K |
17 |
20 |
11 |
- |
|
Anions: |
|||||
|
|
HCO3 |
293 |
192 |
165 |
- |
|
|
SO4 |
85 |
143 |
66 |
192 |
|
|
Cl |
81 |
90 |
121 |
245 |
|
Electrical conductivity dS/m |
- |
- |
- |
1.39 |
|
|
Total dissolved solids |
476 |
591 |
484 |
940 |
|
|
Sodium adsorption ratio |
2.9 |
3.1 |
3.9 |
3.7 |
|
|
Boron (B) |
0.7 |
0.6 |
0.6 |
0.7 |
|
|
Alkalinity (CaCO3) |
- |
- |
- |
226 |
|
|
Total Hardness (CaCO3) |
156 |
200 |
175 |
265 |
|
Source: Asano and Tchobanoglous (1987)
In many industrialized countries, primary treatment is the minimum level of preapplication treatment required for wastewater irrigation.
On-site and laboratory analysis, process analysis, samplers
most important parameter for
successful waste water treatment is
Municipal and industrial applications, research
We research the process to develop our technology
effectively. We are leaders in the process of Dissolved Air Flotation
with our equipment Anaconda. We develop the process with the maxim
precision.